In the complex and rigorous world of electrical systems, every component plays a vital role—some massive, others delicate and yet crucial. Terminal blocks stand out not for their complexity but for their quiet practicality.
Despite their small size, often hidden within control panels or machinery, terminal blocks serve as a crucial bridge in electrical connections. They play an indispensable role in ensuring system stability, safety, and scalability.
What is a Terminal Block?
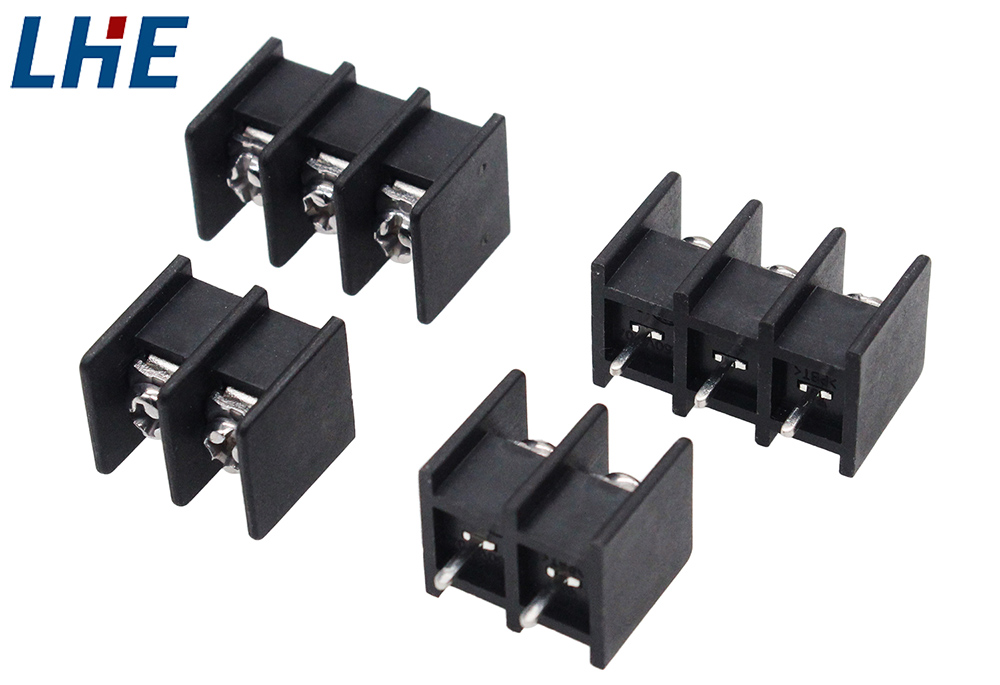
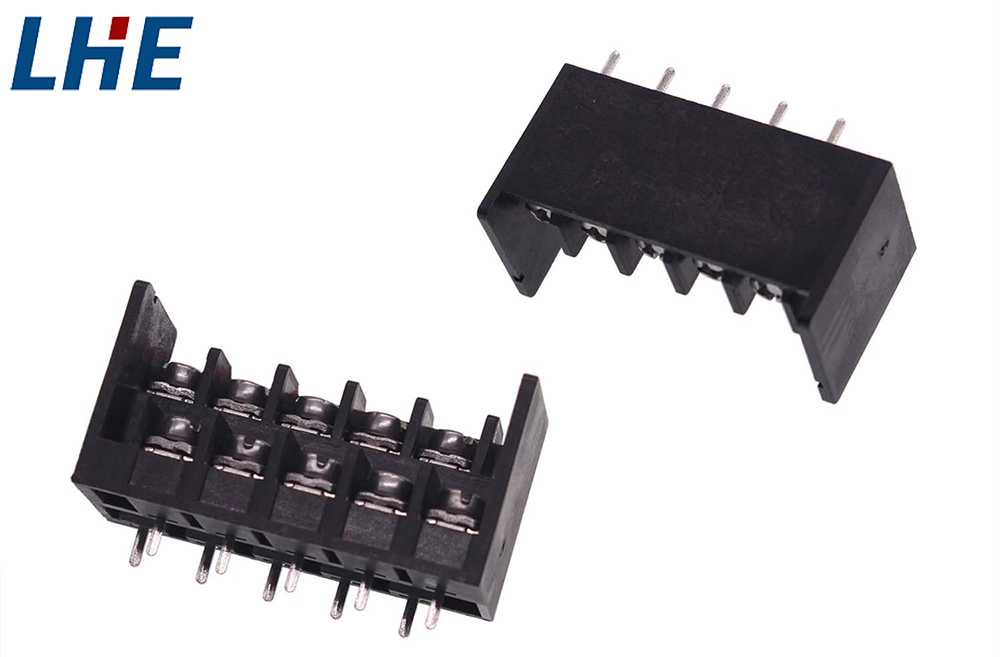
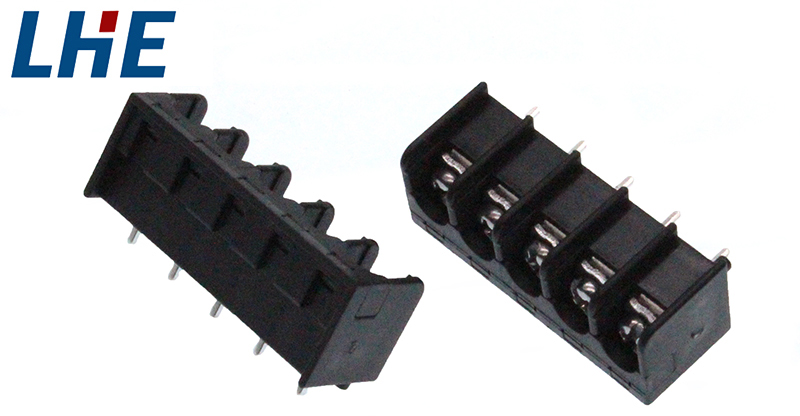
At their core, terminal blocks are modular, insulated connectors used to secure two or more wires together. These terminals typically consist of a plastic housing enclosing a metal terminal into which the stripped end of the wire is inserted and secured—typically with a screw, clamp, or push-on mechanism.
While the concept is simple, the impact is significant: terminal blocks facilitate clean, organised, and secure wiring, reducing the likelihood of loose connections, short circuits, or maintenance complications.
They are typically mounted on DIN rails or circuit boards and serve as connection points between different components of an electrical system. Whether bridging power between devices, distributing signals within control systems, or enabling modular expansion of machinery, terminal blocks ensure everything stays connected.
The Purpose Behind the Design
The primary purpose of a terminal block is to provide a secure and convenient means of connecting electrical circuits. But their usefulness extends far beyond just connection. In industrial settings, terminal blocks are prized for their ability to simplify wiring and maintenance. Instead of soldering or twisting wires together, technicians can connect and disconnect wires with ease, enabling faster troubleshooting and reconfiguration.
Furthermore, terminal blocks help keep systems modular. Organising wires into logical clusters allow sections of a system to be replaced or updated without disturbing the entire setup. This is particularly valuable in industrial automation, where efficiency and uptime are paramount. Their physical structure also offers a degree of safety by providing insulation and spacing between connections, reducing the risk of electrical faults or accidental contact.
Types of Terminal Blocks
There are several different types of terminal blocks, each suited for specific applications. Understanding their differences is key to making an informed selection.